Chemical Formula
After reading this section you will be able to do the following:
- Explain how chemical formulas can be used to describe elements and molecules.
- Identify the chemical formulas for several common substances.
Chemical Formulas
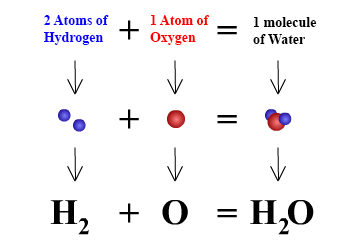
Chemical formulas are used to describe molecules and compounds. In chemical formulas the abbreviations of element names, which are listed in the periodic table, are used. For example, "H" represents one atom of hydrogen and "O" represents one atom of oxygen. If we want to represent two atoms of hydrogen, instead of writing H H, we write H2. The subscript "2" means that two atoms of the element hydrogen have joined together to form a molecule. A subscript is only used when more than one atom is being represented, that is a subscript of "1" will never be seen in a chemical formula. The graphic below illustrates the formula for water using symbols.
Some more common molecules and their chemical formulas are:
Carbon Dioxide -> CO2
Ammonia -> NH3
Glucose/Sugar -> C6H12O6
Isopropyl/Rubbing Alcohol -> C3H7OH
Table Salt -> NaCl
There are millions of known molecules that each has its own systematically assigned name. How these names are assigned is beyond the scope of this module.
Review:
- Chemical formulas are used to describe the types of atoms and their numbers in a molecule or compound.
- The atoms of each element are represented by one or two different letters.
- When more than one atom of a specific element is found in a molecule, a subscript is used to indicate this in the chemical formula.